wHAT IS MOHS SURGERY ?
Mohs micrographic surgery is a highly effective, precise technique used to treat skin cancer, ensuring the removal of cancerous cells while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. This method is particularly beneficial for treating skin cancers in delicate areas where cosmetic outcomes are important. Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the steps involved in Mohs surgery:
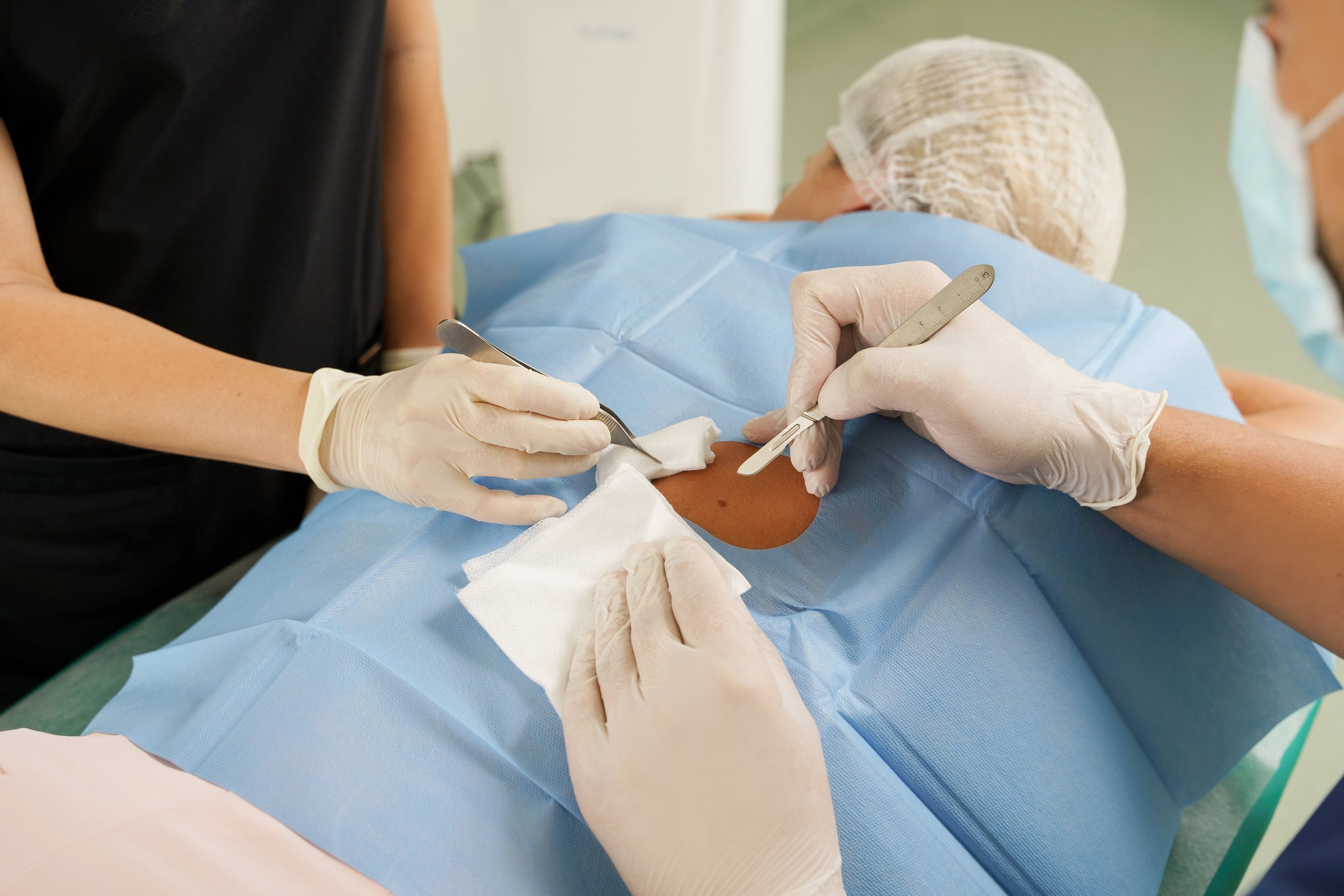
On the day of the surgery, the affected area is numbed with a local anesthetic. This ensures that the patient remains comfortable throughout the procedure while allowing the surgeon to perform precise tissue removal without pain or discomfort.


Once the area is anesthetized, the surgeon removes a thin layer of visible cancerous tissue. This layer is excised with minimal margins to preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
The removed tissue is then carefully marked and mapped to track the exact location of any remaining cancer cells.
Each removed tissue layer is processed in an on-site laboratory, where it is examined under a microscope.
The surgeon meticulously studies the sample to identify any remaining cancer cells. If cancerous cells are detected, the precise location is mapped to ensure only affected areas are treated in the next stage.


If microscopic examination reveals remaining cancer cells, the surgeon removes another thin layer from the exact location of the remaining cancer.
This process is repeated layer by layer until no cancerous cells are detected. This ensures that all cancer is removed while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible.
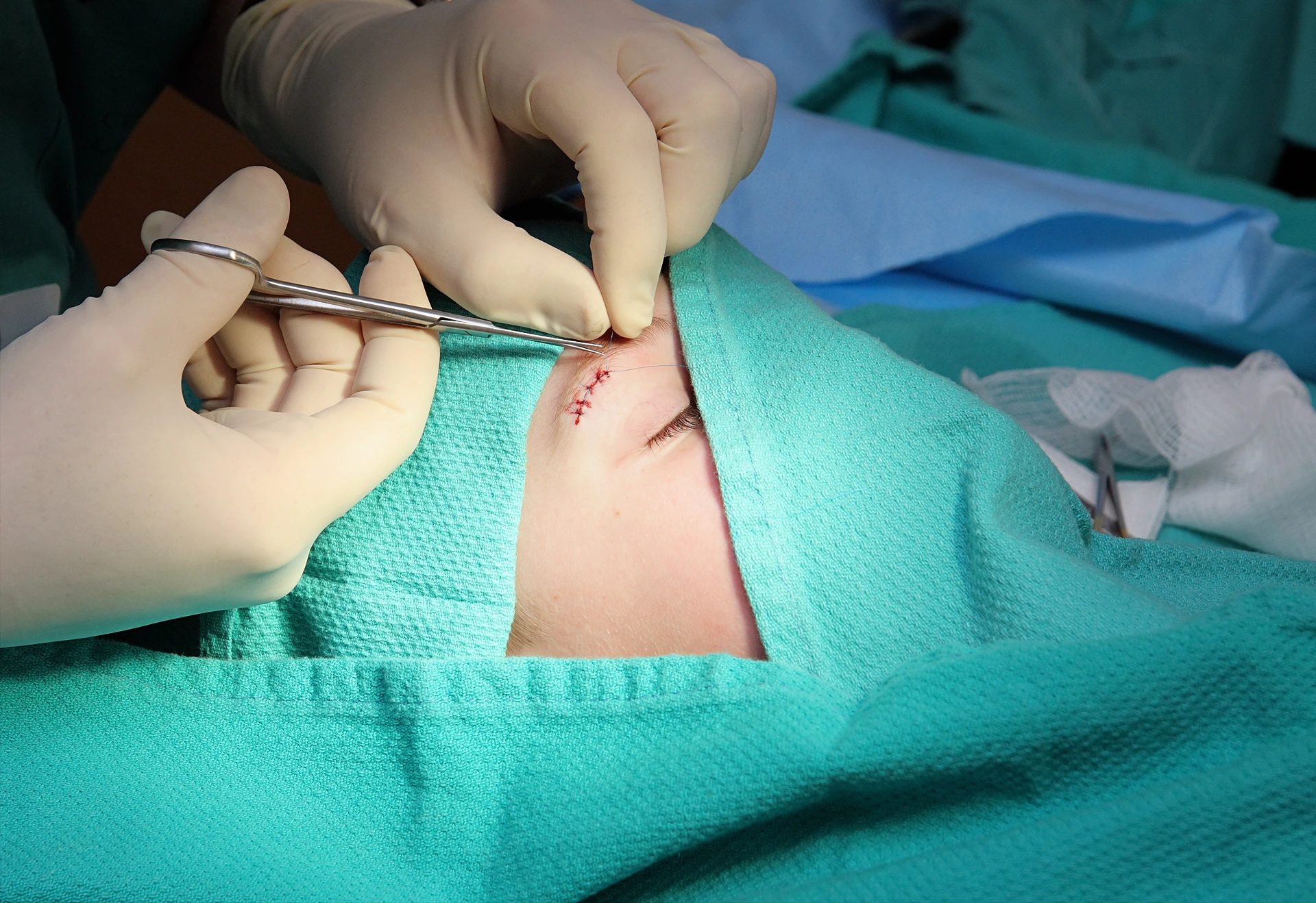
Once the cancer is removed, the next step is reconstructing the surgical site for healing and the best cosmetic outcome.
Reconstruction methods include:
Primary Closure: Small wounds closed with stitches.
Skin Flap: Nearby skin repositioned for a natural look.
Skin Graft: Skin taken from another area to cover large defects.
Secondary Intention: Wound heals naturally over time.
The surgeon chooses the best method for function and aesthetics.